Now that we have established a foundation of how circuits can be built, we are ready to begin an exploration of how a processor can be weaved from some core components into something truly magical. We will begin our discussion on the building blocks of processors with a brief discussion of current flow across components. Starting with our base example from A Practical Introduction to Electrical Theory.

In this example, we can see that current flows from the battery to the bulb, and again from the bulb to ground. But what happens if we flip this circuit?
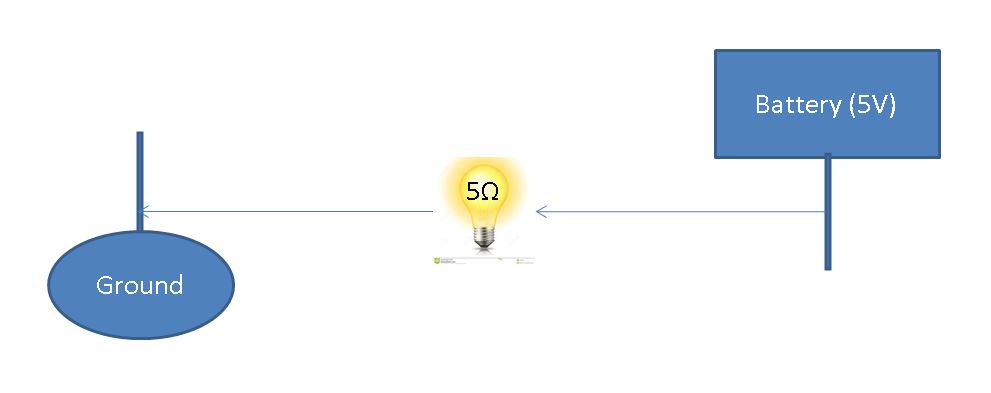
We can see this circuit looks the same as our base example, only switching the location of the battery and ground. And indeed it does behave the same for a simple resistor! But seeing this we can’t help but wonder, is this always true? Is it possible for a component in a circuit to work when the current is going in 1 direction, and behave differently when the current is going the other way?
The answer to our question is yes. One example of such a component is a diode. A diode has the property of easily allowing current to flow in 1 direction, but strongly resists current flow in reverse. For a better intuition of how exactly a diode does this, looking at a diagram may be useful.
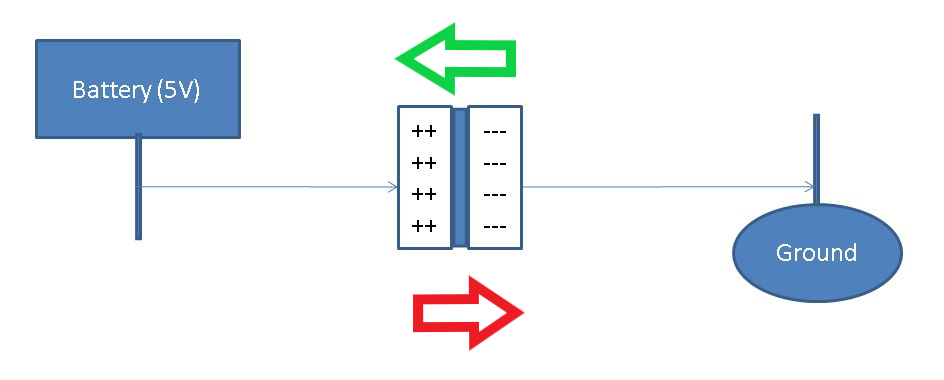
In the above example, the middle block represents a PN diode. This consists of 3 sections, a positive segment which easily accepts current, a negative segment which repels current, and a neutral insulation between the two layers.
Because the negative segment repels current, we can see current will only flow readily away from negative (into positive), and there will be some effort to move current from positive to negative. In fact flowing in reverse is even more difficult than it sounds! Overcoming the neutral insulation in the natural direction is ~0.5 Volts. To get current to flow in the reverse direction is ~6 Volts. An almost 12-fold increase in potential required!
Diodes are among the most essential components of circuitry and are used in transforming alternating currents into direct currents (rectifier), protecting components from voltage spikes, and can even be used to build limited logic circuits! While interesting to note, there are some clear issues with diodes for the purpose of more complex circuits.
- The diode depends on the direction of the current for operation characteristics. This significantly limits options in terms of design.
- A diode has no means of amplification because the input is tied directly to the output. This makes it difficult to provide power to all components in any sizable circuit.
Luckily, there is a component which fills the gaps present in diode-based circuitry, the transistor. A transistor is a component with an input, output, and a control. The defining property of a transistor is that modifications to the control can impact the output. A diagram may be useful in helping us to better understand transistor operation. Below we include snapshots of a transistor in 3 states each applying some modification to the control voltage.
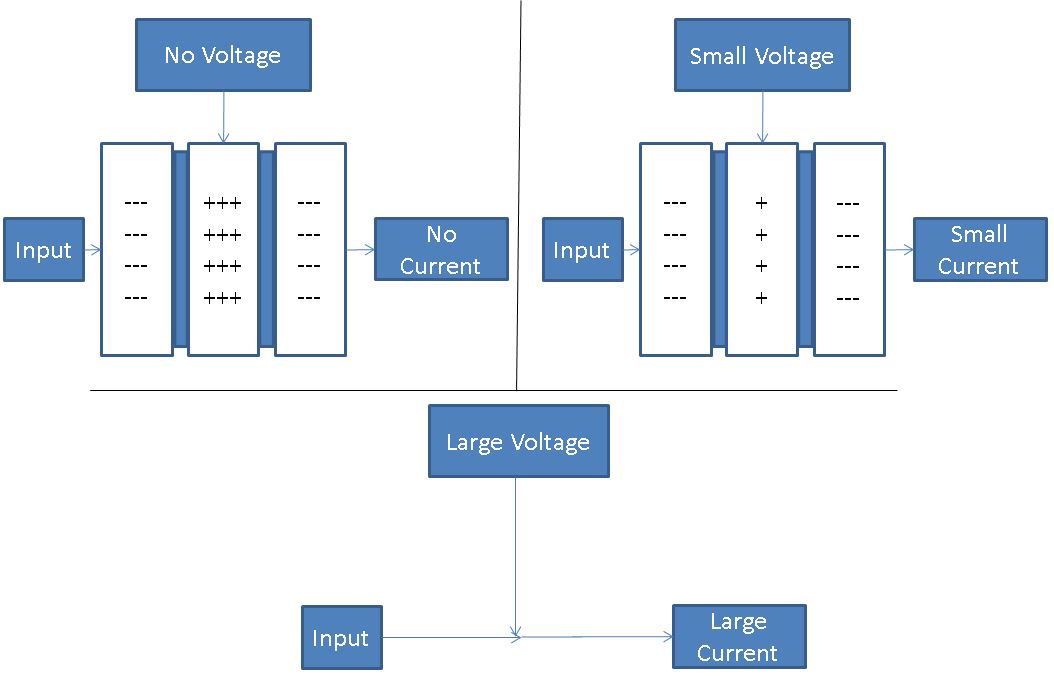
Physically, a transistor looks similar to a diode but with the addition of an extra positive or negative layer. By changing the voltage at the middle layer, we can make current flow more easily from Input to Output. In this way, a transistor behaves as a resistor from input to output which can be dynamically modified by an external source. Also, the control input provides a natural mechanism to introduce more current into the circuitry that follows. Truly amazing!
Discussion:
In this section, we discussed the components needed to update simple circuits with the capacity to model Boolean logic. One question we haven’t answered is: Why does this matter?
In a sense the title of this article is a bit misleading. Yes, transistors are the building blocks of processors, they are also a foundation for memory, data IO, and almost any operation a computer can perform. While isolated from the software front, the impact that improvements at this level have can be substantial. As more transistors can be included on a single chip, there is the capacity to add more optimized supporting infrastructure such as larger caches and smarter branch prediction.
